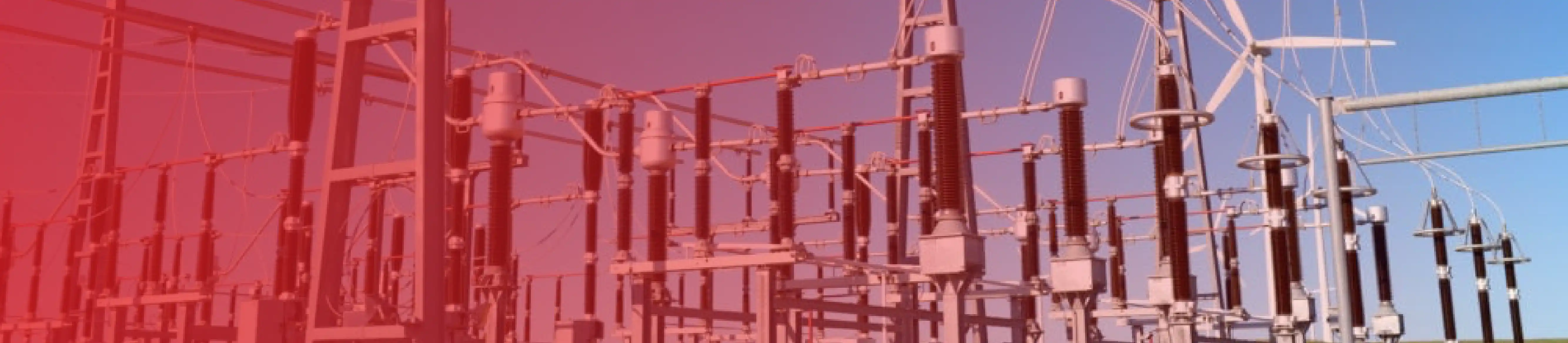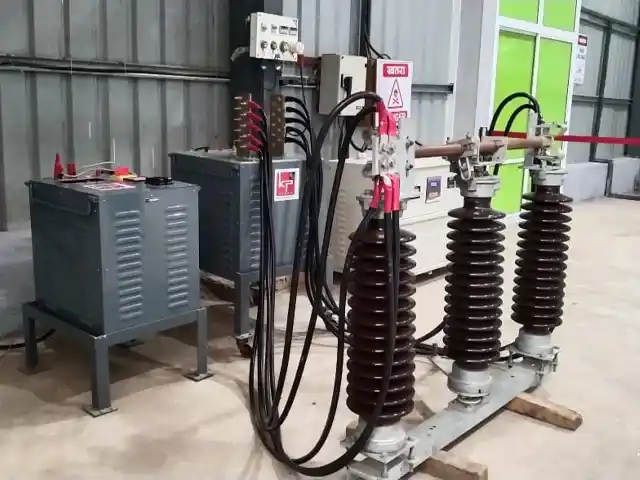
The Role of Substation Structures in Power Distribution
Substations represent the very heart of the electrical grids, mapping the way to safer, cheaper, and more effective energy usages by stepping-down the voltage levels from the transmission to the distribution network for supplying the end-users. The instrumental value of the substation structures in power distribution: they enable smooth functioning of high-tech gear, accomplish system trustworthiness, and assure user security under any operational and environmental circumstances.
India is currently undergoing a period of fast change in its energy sector. To meet the ever-growing demand for electricity, facilitate more renewable energy sources, and work with the innovation in power distribution systems of transmission, the infrastructure of substations has never been so important. It would be impossible for the modern substation technologies in India, as among others, gas insulated switchgear (GIS), hybrid substations, and smart monitoring systems to function well without providing a great job the solid and well-constructed station structures.
The latter set is essential for the smooth running of the pieces of equipment like transformers, circuit breakers, busbars, and protective relays whose weights are often very difficult to bear and whose operation must be without any failures under the challenge of heavy electrical loads, environmental stress, earthquakes while allowing the necessary adjustments. In short, the role of substation structures in power distribution help with energy sustainability, safety and efficiency.
Such a requirement has become even more important during the period 2025-2026, where substations are expected to provide support for quick deployment infrastructure for emergency power systems as well as temporary renewable energy farms during grid contingencies or disaster recovery operations.
Understanding the Importance of Substation Structures in Power Systems
Substations are the main nodes of the power networks, not only do they regulate voltage levels but they also control the power flow from the generation plants to the distribution networks. The structures in these substations have different functions:
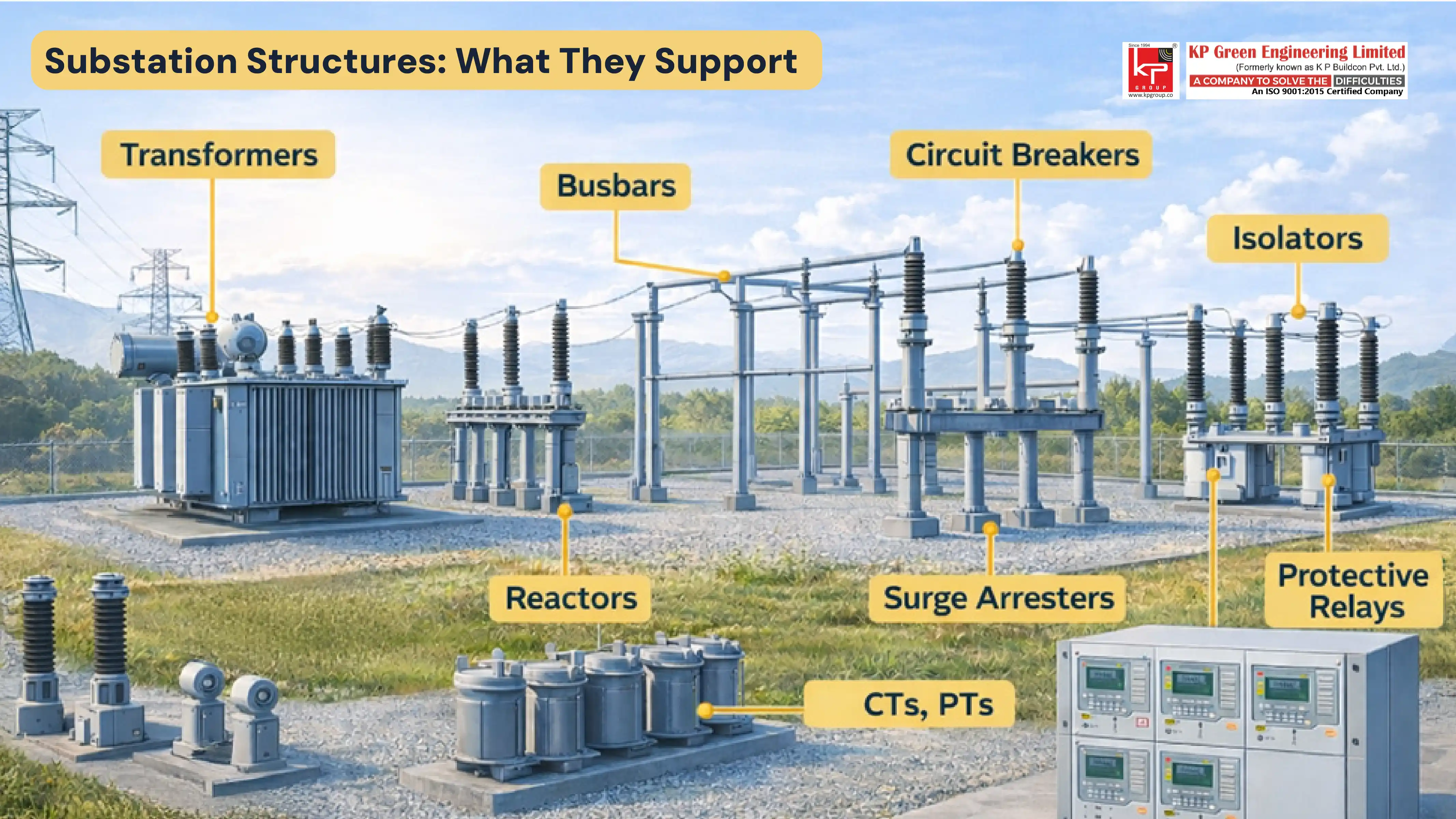
- Physical Support for Electrical Equipment: Substation structures are where the heavy transformers, isolators, circuit breakers, and busbars are mounted on. Without solid and properly designed frameworks, these parts cannot work in a safe or efficient manner.
- Operational Safety: Electrical equipment is extremely high voltage, very often above 765 kV for AC systems and ±800 kV for HVDC systems in India. Substation structures uphold the correct distances, avoid short circuits, and at the same time, allow maintenance staff to safely carry out their jobs.
- Grid Reliability: Careful structural planning is what makes continuous power supply possible. A fault or structural failure in a substation may cause a blackout that affects a large area. Structures designed to resist such environmental stressors as wind, seismic activity, and corrosion, contribute greatly to system reliability.
- Flexibility and Upgradability: Thanks to the grid modernization in India, substations are now required to support hybrid energy systems, smart grid technologies as well as the renewable energy increasing trend. Properly designed substation structures provide the freedom of equipment relocation, extension, and future upgrade without the need for a long period of downtime.
- Support for Modern Technologies: Advanced functionalities of the substation– SCADA systems, require that the equipment be there precisely and be supported. Without the structural backbone, these systems would not perform optimally.
The importance of substation structures in power systems is foremost of a power system’s foundation: they underpin grid efficiency, safety, and innovation. The expansion of the Indian power network will not only be a challenge for the country itself but for the role of substations and their supporting structures.
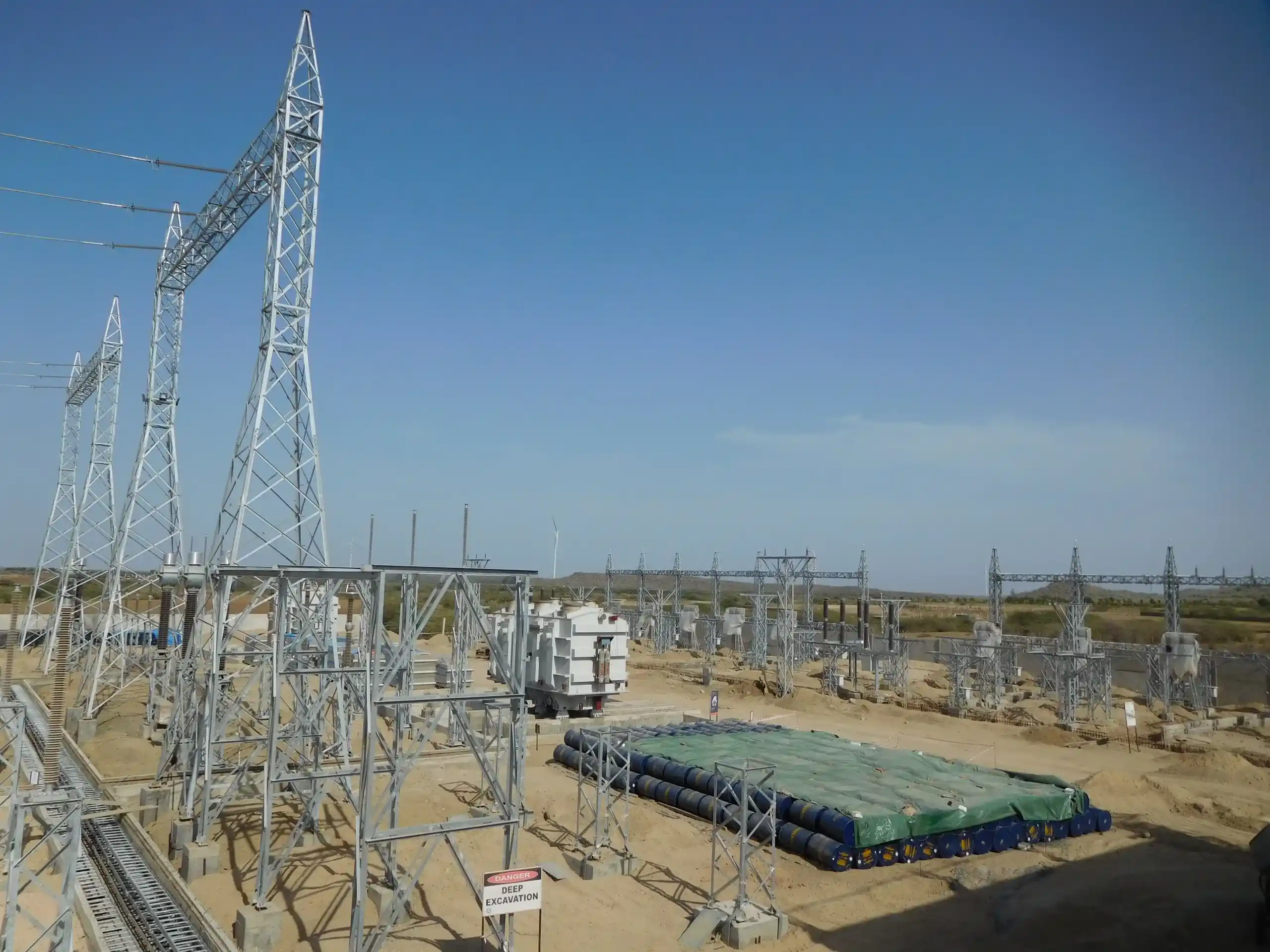
Types of Substation Structures Used Across India’s Power Grid
Substation structures in India are influenced by voltage levels, weather conditions, and changes in the design. The types of substation structures can be categorised into steel, gantry, and support structures for transmission and distribution networks. Each of these types performs different operations, contributing to energy safe, reliable, and efficient distribution.
Steel Structures Used in Substations
Steel continues to be the leading component for substation constructions over a period of time, because of its high strength, long life, and flexibility of use. They employ the metal framework to present the heavy electrical equipment, environmental stress, and upgrading of devices for the needs.
Some of the main points of the steel structures used in substations are:
- Load-Bearing Capacity: A transformer, a busbar, and a switchgear might be each heavy till tens of tons of weights. The steel frameworks are thus brought up to proper support of such weights while securing them under dynamic conditions as well.
- Environmental Resilience: The steel building constructions along with the alike are made defensively against rust and they can suffer from extreme climate and still alive. Such conditions as high wind, hefty rain, and high temperature are no threat for them. Besides that, in areas that are hit by seismic disasters, their reinforcement is setup so that the failure mode is not a complete one.
Most of these structural designs are normally checked through sophisticated engineering software like STAAD Pro and PLS-Tower, which allow detailed simulations for the extreme weather conditions that include 50 m/s wind speed, seismic load, conductor tension forces, and according to prevailing Indian and international standards. They further tend to build clients’ trust. - Modular Design: Commonly, a modular form is preferred in the latest substation designs that allows the unit to be put together very quickly, the time for the building is cut down significantly and it is easy to expand. This feature of modularity finds local application in urban substations where there is a shortage of space.
- Integration with Modern Technology: Besides the basic assembly work, metal buildings accomplish the necessities of engaging the smart technologies by providing easy access points for sensors, communication networks, and automation gadgets that lead to the use of Smart Grid and predictive maintenance.
In India, steel structures are used throughout an AC substation (132 kV to 765 kV), HVDC substation (±320 kV to ±800 kV), and distribution substation (33 kV and below). The material's strength and the precision of the design are contributing elements that guarantee user safety, operational efficiency, and a long service life.
Substation Gantry Structures and Equipment Support
Gantry structures are designed to help the arrangement of the electric components structurally within the substation. These devices lift busbars, isolators, and other high-voltage units above ground level thus ensuring safe clearances and facilitating maintenance activities.
The listed benefits of gantry installations are:
- Space Efficient: The use of gantries permits the leveling of the components one above the other and, it is very important being able to do this in a limited place such as substations which are especially common in towns with a high concentration of inhabitants.
- Access to Maintenance: Through the use of the upward-facing gantries there is no visiting of the maintenance staff and only the equipment is exposed to inspection, servicing, and upgrade possibilities, thus production hour losses are nearly reduced to zero.
- Operational Safety: The adoption of appropriate distances and the realization of organized support are some measures that largely eliminate the possibility of human contact, short circuits of the device, and operational injury risk.
- Load Distribution: By the use of the respective device do the loads that result from the weight of the parts get evenly spread thus the foundation of the substation is relieved of pressure and structural fatigue is minimized.
Substation gantry structures and equipment support are part of both transmission and distribution networks. In addition to supporting AC and DC systems, they also provide the means for the hybrid-ready substations that facilitate the integration of renewable sources of energy. The design of this device is usually guided by the CEA standards, IS codes, and IEC regulations thus reliability and conformity are assured.
Substation Support Structures for Transmission & Distribution Networks
Transmission and distribution substations are the essential instruments that connect the generation plants to the consumers. In these substations, support structures are the mainstay of the most heavy-voltage equipment, as well as the conductor alignment, weather, and electrical stress resistance.
Some key points they handle:
- High-Voltage Load Handling: In such conditions do these buildings/frames have the task of performing the carrying of the said conductors from as high as 132 kV to 765 kV (AC) or ±320 kV to ±800 kV (HVDC) without structural deformation, safely.
- Seismic and Environmental Safety: Apart from the features that allow the structures to perform the given task of transferring the power under those circumstances safely, there are more traits that assure power continuity. More specific are these safety ones that are caused by the already mentioned earthquakes, cyclones, lightning strikes, and temperature changes, etc., thus the power supply will never be interrupted no matter the nature of the occurrence.
- Material and Design Standards: For instance, steel, galvanized metal, and reinforced concrete are taken up depending on voltage level, soil conditions, and environmental exposure. The design complies with ISI codes and CEA regulations.
- Modernization Adaptability: As India moves to adopt renewable energy sources, hybrid substations, and Smart Grid technologies will have to be the support structures permitting flexible equipment layouts, easy replacement, and upgrade routes.
Substation support structures for transmission & distribution help to keep the grid stable, lower transmission losses, and provide for the safe and efficient distribution of power throughout India's diverse network needs.
Electrical Substation Design and Components That Influence Performance
With developing one of the fastest-growing electricity grids in the world, the attention is going beyond just increasing the capacity to creating substations that maintain long-term efficiency, fault tolerance, and operational intelligence.
Electrical substation design and components have changed to be more than just the basics of stepping up or stepping down the voltage. Presently, substations are built to be power flow control hubs, reliability enablers, and grid automation centers. Their design has a direct bearing on the performance, safety, O&M costs, and future scalability.
Compared to older legacy substations that were designed based on fixed load assumptions, the current electrical substation design concept takes into consideration modularity, asset life extension, compact layouts, remote diagnostics, safety measures, and multi-directional power flow. With India having an increasingly complex mixture of power inputs– thermal, hydro, solar, wind, biomass, green hydrogen pilot nodes, and storage technologies, the role of substations has become extremely dynamic. They are not only the ones that route power but also manage quality, mitigate outages, protect grid assets, and balance load fluctuations.
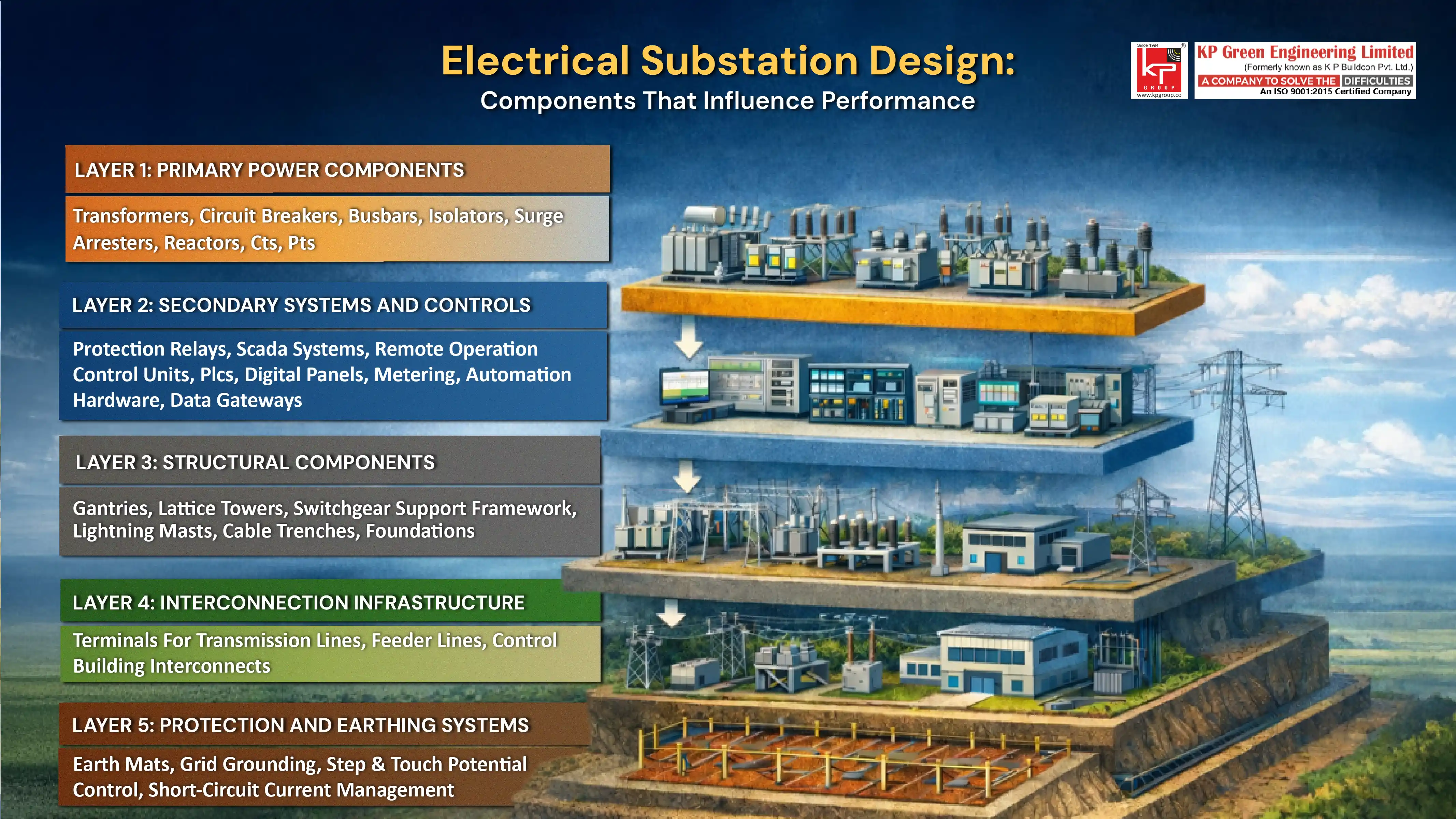
Essential Electrical Substation Design components that define performance are–
- Primary Power Components: Essential primary power components that are to be found in any power system include transformers, circuit breakers, busbars, isolators, surge arresters, reactors, current transformers (CTs), and potential transformers (PTs).
- Secondary Systems and Controls: Examples of secondary systems and controls are: protection relays, SCADA systems, remote operation control units, PLCs, digital panels, metering, the automation hardware, and data gateways.
- Structural Components: Structural components are elements that are used for building the support frameworks of the main power system: gantries, lattice towers, switchgear support frameworks, lightning masts, cable trenches, and foundations.
- Interconnection Infrastructure: Terminals for transmission lines, feeder lines, and control building interconnects are three of the most important parts of the interconnection infrastructure.
- Protection and Earthing Systems: Protection and earthing systems consist of earth mats, grid grounding, step, and touch potential control, and short-circuit current management.
The combined outcome of all these components is a site that demonstrates operational characteristics of a smart, programmable, load-stabilizing asset.
Substation Structural Engineering Standards and Safety Guidelines
Substation structural engineering standards and testing follow the strictest standards among the power infrastructure. The use of standards has two main roles– Firstly, they set the mechanical and safety requirements at the minimum level. Secondly, they assure that the system will perform correctly both under normal and abnormal grid conditions.
Core Structural Engineering Considerations:
- Mechanical Strength and Stability: The structures must be able to resist: Wind pressure, earthquake shocks, short-circuit currents, conductor tension, equipment weight, thermal expansion, vibration and dynamic loads
Essentially, all those structures that are part of high-voltage substations such as gantries, towers, and equipment supports have to be detailed and manufactured in such a way that they can survive the short-circuit forces that cause the intense mechanical stress of the fault area. - Corrosion Protection and Material Durability: India holds a variety of environments such as the dry desert, a humid coast, arid cold mountainous regions, or hot and dry plains. Structural designs have to be sensitive to these condition changes; therefore, they must rely on materials such as: Galvanized steel frameworks, weather-resistant coatings, hot-dip zinc treatment, rust inhibitors, moisture and UV-resistant paint systems
- Grounding and Lightning Protection: Grounding design is definitely the safest device of substation engineering. Reinforced meshes provide the safety of touch voltage, fault dissipation, and equipment protection by ensuring that the area where it is applied is not hazardous.
Flying masts, shield wires, and surge protection systems are the first line of defense against the overheating and breaking down of the power system components because of the lightning. They prevent the spread of the faults and the resulting outages across the power network.
How Substation Structures Enable Innovation in Power Distribution Systems
Power substations of the present are no longer just passive electrical routing stations but have turned into highly capable nodes of the system that power the modern grid. The change is majorly influenced by the changing requirements of electricity, the integration of renewables, and digital power management. Substation frameworks are being remodeled to serve as platforms for innovations in power distribution systems.
The Innovation Drivers Are Clear:
- Digitalization: Automation is enabled through intelligent electronics, and sensors facilitate real-time data exchange, predictive maintenance, and remote control.
- Grid Intelligence: Presently, software controls and smart grid components perform the tasks of switching, fault isolation, and load synchronization automatically.
- Grid Flexibility: Fast and extensive integration of: Solar on rooftops, solar parks for industry and grid-scale, wind farms, battery storage, EV charging corridors, put a heavy load of expectations on substation structures in terms of their capability to respond to a rapidly diversifying power ecosystem.
- Asset Optimization and Cost Reduction: Modern substations are capable of reducing O&M downtime, enhancing equipment utilization, and preventing the premature replacement of equipment.
- Safety and Reliability: Structural innovation has played the role of a reliability provider as India attempts to develop a power sector that is more resistant to extreme weather events, cyber threats, and demand uncertainty.
Smart Grid and Modern Substation Infrastructure
The smart grid revolution is fundamentally turning the role of substations to that of the operational intelligence centers. They maintain linkage with: Central load dispatch centers, IoT-based monitoring systems, distributed renewable energy, remote switching controls protection relays, energy storage management.
Smart substations generally feature:
- Digital protection technology.
- Advanced switchgear.
- Data-driven power management.
- SCADA communication.
- Microprocessor-based relays.
- IoT-enabled monitoring.
The result is a substation that takes on the automation of many of the most vital grid functions– manual operations and inspections that were performed by humans are now under algorithmic control.
Smart Grid and modern substation infrastructure enable:
- Acceleration of fault identification
- Predictive failure detection
- Improved power quality management
- Reduced outage duration
- Increased grid efficiency
The end result is not only that of operational efficiency but of a smarter power ecosystem.
Modern Substation Technologies in India Transforming Reliability
In the worldwide competition to have a high-tech substation infrastructure, India has become a trend-setter. A range of new technologies is being implemented at the level of the grid (both the transmission and the distribution networks).
Key points of modern substation technologies in India:
- GIS substations for urban and industrial areas.
- Hybrid AIS-GIS substations.
- Advanced protection and automation systems.
- Digital and unmanned substations.
- Condition monitoring sensors.
- Gas-insulated and modular switchgear.
- Substations designed for renewable power integration.
- Substations with storage and hybrid grid capacity.
They are mainly revolutionary because their focus is on reliability i.e., they depend upon direct interaction with the user. Unlike old substations that were just one-direction-guide-power-flow, modern substations are multi-source dynamic power-routing capable.
Technologies enhancing reliability in India: Digitized SCADA integration, advanced fault current limiting devices, intelligent EPC-61850-Based Electronic Devices (IEDs), remote and unmanned monitoring, condition-based maintenance systems, high-grade insulation and switchgear, fire-safe transformers and reactors. high-reliability busbar and feeder designs.
The change is evident everywhere– from renewable energy corridors to smart cities, green hydrogen clusters, and industrial zones.
Strengthening Grid Stability: How Substation Structures Improve Reliability and Safety
Reliability and safety in power distribution depends on the structural engineering of substations just as much as the quality of the electrical equipment. Strong and well-designed substation structures are central to how substations improve grid stability, they not only stop outages from spreading but also allow the isolation of faults that have not yet been extended to the larger power network. Nowadays, substations have sturdy gantries, shock-absorbing supports, arc-flash protection, highly reliable grounding, and safe conductor routing to maintain operational stability.
Some of the features like lightning and surge protection, safe clearance zones, and remote operation systems lessen the need for manual intervention and thus, increase the continuity of the grid. Moreover, structural engineering is assisting the grid by focusing on safety in the component placement and design. Control of touch and step potential, anti-collision support structures, controlled fault pathways, weather-resistant materials, and short-circuit-rated steel frameworks are some of the ways that ensure power stations are safe during extreme operating conditions.
While poorly constructed structures might lead to serious risks of unreliability, substations that are well-built and engineered become a source of power flow stabilization and the network's protection even in a major fault or environmental stress situation.
The Future of Substation Structures for India’s Growing Renewable Power Landscape
India's move towards an energy mix that is heavily renewable-based requires new substation structures of the next generation which are designed for the future grid.
With increasing solar and wind capacities, substations are getting transformed into renewable-ready substations, hybrid-ready grid structures, and next-gen substation designs that can store energy, support multi-directional power flows, and do real-time energy balancing.
There are also modular and compact substations for space-limited urban areas, GIS and hybrid AIS-GIS configurations, high-capacity transmission nodes, and substations combined with battery energy storage to mention some of these developments.
Moreover, these innovations facilitate the implementation of AI-enabled monitoring, advanced protection systems, and predictive maintenance that result in increased reliability and efficiency.
By such changes in their structures, power networks become capable of coping with variable renewable inputs and of incorporating future technologies like EV charging, green hydrogen infrastructure, and distributed generation. Substation structural engineering will be instrumental in India’s grid transition next as it will involve the creation of designs that are not only more intelligent but also more durable and flexible–systems that can perform decision-making automatically, be resistant to higher fault levels, and be able to grow along with the increasing energy demand.
Frequently Asked Questions:
About Us
KP Green Engineering Ltd. provides complete engineering and steel structure manufacturing solutions worldwide, serving industries such as renewable energy, telecommunications and beyond.
Get In Touch
Latest News
KP Green Engineering Scales Durable, Low-Carbon Infrastructure
KP Green Engineering bags landmark order worth Rs 819 crore from BSNL for 4G telecom infrastructure
Gujarat Deputy CM Harsh Sanghavi Inaugurates KP Green Engineering's Matar Facility


















